The Internet of Things (IoT) is at a crossroads in terms of energy consumption and more questions about whether traditional sources of energy are capable of supporting its growth are being raised. Because of this, more manufacturers are turning to alternative sources of energy combined with low−power connectivity because it has significant market potential.
One new approach is harvesting dynamic energy from the movement and force applied to a button operating like an ON/OFF switch. The benefits provided by wireless, battery−free switches are obvious and address the top concerns of IoT manufacturers − ease of implementation and power consumption.
These devices offer unparalleled flexibility for deployment within buildings because they do not require any hardwiring. They can be fixed onto the wall or movable. They also remove the maintenance hassles and environmental impact of battery replacement and disposal. This environmentally friendly system has numerous advantages. You have the flexibility to install a switch without cabling in any location you want, where it will fulfill its function over the entire length of its service life without any maintenance or battery changes. In contrast to information transmission via cables, the self−powered wireless switch is also attractive for building services because it is easy to retrofit.
For example, you can install new light switches without having to cut any holes in the wall. There are also numerous possibilities for use in industrial automation, particularly when the time it takes to lay cables is disproportionate to the application. Here again, the energy harvesting wireless switch serves as a cost-effective, battery−less alternative to cable−based micro−switches.
The physical design of the switch is also made much easier, enabling creativity and new design styles that have never been considered previously.
A key factor in making this eco−friendly application a reality is ensuring that the wireless protocol used are conducive to the low−power nature of the switch. One option is the Green Power™ protocol offered by the Zigbee Alliance™.
Green Power Protocol by the Zigbee Alliance
Designed for optimized energy consumption and even energy harvesting, the Green Power protocol from Zigbee Alliance offers great potential within industrial IoT for applications including connected lighting and building automation. With its long-range connectivity, the Green Power protocol is easy to deploy in larger buildings, provides flexible deployment and reconfiguration options, and is compatible with all new building trends with its eco−friendly and low power design.
For low power applications, the Green Power protocol offers numerous advantages that can positively influence communication range, including:
• Using a spread spectrum instead of Fast Frequency Hopping (FFH) for improved range
• Lower bit rate (250 kb/s) for improved sensitivity performance
• Higher Tx power (8 dBm)
• Using a less crowded wireless spectrum
Strata Enabled Zigbee Green Power Kit
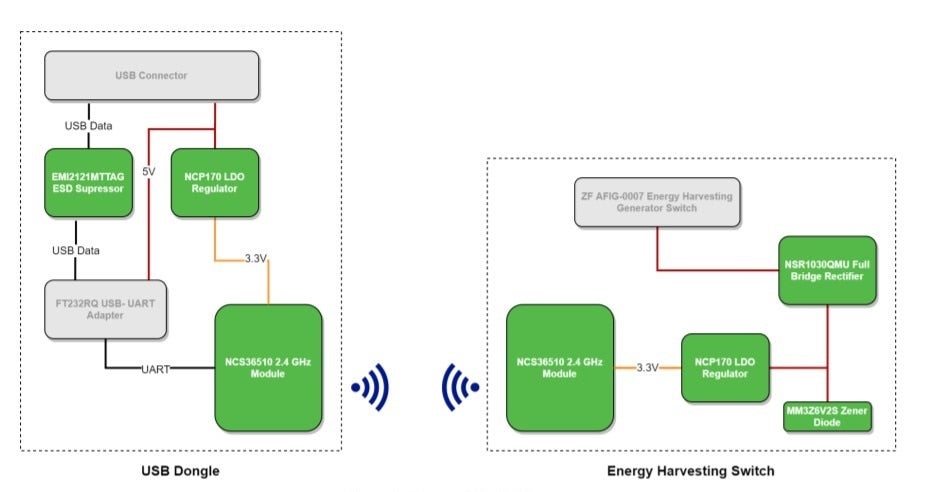
The Strata Enabled Zigbee Green Power Kit demonstrates the use of NCS36510 in a battery−free Zigbee Green Power application. The kit consists of one Zigbee Coordinator (ZC) USB device, which interfaces with the Strata Developer Studio™, and two energy harvesting nodes, which act as Zigbee Green Power Devices (ZGPD). The Strata Developer Studio features a virtual development environment of a modern smart home and simulates both a Zigbee 3.0 lighting system and a security sensor on the door. a superb user interface with vBy pressing the ZF switch on each of these devices, energy is generated and used to power the NCS36510. The Zigbee Green Power Kit design consists of an energy harvester, a simple diode rectifier bridge, a clamp, a small 56 micro farad storage capacitor, as well as the NCS36510 transceiver.
Figure 3. System Overview of the Strata Enabled Zigbee Green Power Kit
Strata Enabled Zigbee® Green Power Kit
Learn more about the Strata Enabled Zigbee® Green Power Kit, or check out our Development Resources below!
Development Resources
Be sure to subscribe to our blog and follow us on social media to receive the latest updates on our technologies, solutions and company news!
Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram | YouTube